Railway and it components
Railway and it components
Railway Engineering is the branch of transportation engineering where latest technology is used for the development, design, construction and maintenance of railway tracks for the safe, efficient and economical movement of rail traffic which include both passenger and goods train.
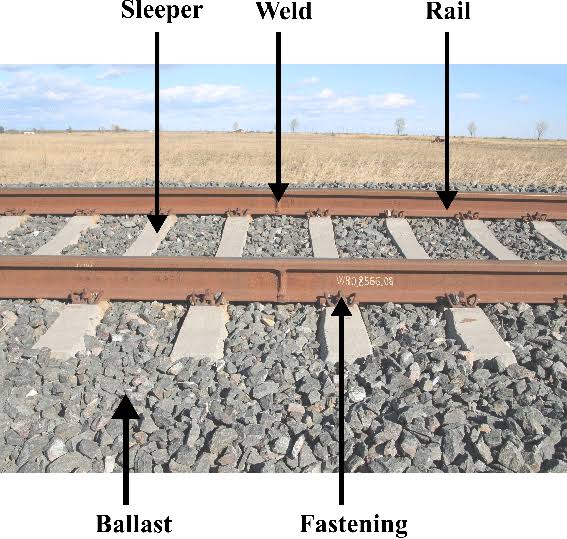 |
| Components of railway track |
Components of Railway Track
Gauge
Gauge is the distance between the inner edges of a pair of rails. There are three types of gauges used in Indian Railway System -
Narrow gauge - 762 mmMetre gauge - 1000 mm
Broad gauge - 1676 mm
98% of railway track is using Broad Gauge System.
Rail
Rail is the main component of railway track and provide hard and smooth surface for running of trains. The rail section is of three types double headed, bull headed and flat footed. The rail section is generally made of high carbon steel having high tensile strength. The Broad gauge rail section is of three types :- According to weight 60 kg, 52 kg and 19 poundsThe length of the single rail in Broad gauge system is 13 metre.
Rail joints
Various rails are joined together to form a smooth railway tracks. There are two ways of joining the rails that is by welding or by using fish plates and fish bolts. Fish plates are metal elements which are bolted to the end of rails using fish bolts.Rail fastening
Rail fastening are fitting which are used to fix rails to sleepers. Spikes and clips are used for this purpose. A rail spikes a big nail that has an offset head and it is used to clamp the base plate with the sleeper. There are three types of Spike i.e., is dog spikes, round spikes, and screw spikes.Clips
Clips are used in concrete sleepers to connect the rail with the sleeper. They are composed of silicon steel rod 20.6 mm in diameter and each sleeper required 4 clips.Sleeper
Sleepers are the member placed under the rails in transverse direction to transmit the load from the railway wagon and coaches through the rails to the formation.Function of sleeper
- To support the rails firmly specially on turn out and crossing.
- To hold the rail in place at a given gauge and at inward slope of 1 in 20.
- To transfer and distribute the load to the stone ballast or concrete block.
- To provide an elastic medium between the rails and ballast and to absorb the vibration.
- To maintain the alignment and superelevation of the track.
- To provide stability and stiffness to track.


Comments
Post a Comment
Please write your views and suggestions.